resultant velocity|resultant speed formula : Bacolod Learn how to solve problems calculating an object's resultant velocity from its components using trigonometry and the Pythagorean Theorem. See examples of boat and plane . This Boeing 777-200LR seats 238 passengers in a three-class configuration and is primarily used on long-haul routes. There are 8 flat bed seats in First Class, 35 anlged-flat seats in Business, and 195 standard Economy Class seats. . All the Seats on AI 777-200 lack lumbar and neck support. The extra legroom is of no use when your back is .
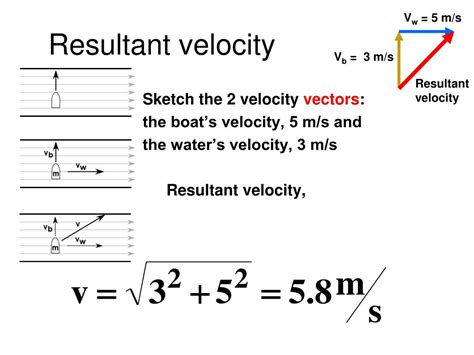
resultant velocity,Learn about the concept and applications of resultant velocity, the sum of the vector velocities of an object or a fluid. Find examples, formulas, and references from various fields of mathematics and physics. 117. Share. 25K views 3 years ago. How to Calculate Resultant Velocity. Part of the series: Physics Education. Calculating resultant velocity can be accomplished through the . Learn how to find the resultant velocity of a boat traveling in a river by adding the velocities of the boat and the current. See the video transcript, visualization, and questions with .Learn how to solve problems calculating an object's resultant velocity from its components using trigonometry and the Pythagorean Theorem. See examples of boat and plane .
OpenStax. Learning Objectives. Explain the concept of reference frames. Write the position and velocity vector equations for relative motion. Draw the position . We see the average velocity is the same as the instantaneous velocity at t = 2.0 s, as a result of the velocity function being linear. This need not be the case in . The resultant velocity refers to the overall velocity of an object when multiple velocities are combined. It is the vector sum of all the individual velocities. When . Nated Engineering. 8.69K subscribers. Subscribed. 354. 24K views 3 years ago Engineering Science N4. IN THIS VIDEO WE LOOK AT RESULTANT VELOCITY. WHAT IS RESULTANT VELOCITY AND .
tan. θ = v y v x. What if we need to relate the components to the other angle? sin. ϕ = opposite hypotenuse = v x v. cos. ϕ = adjacent hypotenuse = v y v. tan. ϕ = opposite adjacent = v x v y. Note that the v s in these . In this video, the concept of how to combine the correct velocity vectors is discussed. Two examples are worked out to show how to solve for the correct hor. in this video we look at resultant velocity. what is resultant velocity and how to calculate resultant velocity for questions concerning velocity that is act.
We can add the two velocity vectors to find the velocity of the person with respect to Earth. This relative velocity is written as. v PE = v PT +v TE. (4.6.1) (4.6.1) v → P E = v → P T + v → T E. Note the ordering of the subscripts for the various reference frames in Equation 4.6.1 4.6.1.The resultant is the vector sum of two or more vectors. It is the result of adding two or more vectors together. If displacement vectors A, B, and C are added together, the result will be vector R. As shown in the diagram, vector R can be determined by the use of an accurately drawn, scaled, vector addition diagram.The resultant velocity of the motorboat can be determined in the same manner as was done for the plane. The resultant velocity of the boat is the vector sum of the boat velocity and the river velocity. Since the boat heads straight across the river and since the current is always directed straight downstream, the two vectors are at right angles .resultant speed formula Learn how to calculate the resultant velocity vector in standard position. https://sites.google.com/site/swtcmathSection 4 Part 1 Homework Solutions Video fo.a plane flying due east at 200 km/h encounters a 40-km/h wind blowing in the north-east direction. the resultant velocity of the plane is the vector sum v = v1 v 1 + v2 v 2, where v1 v 1 is the velocity vector of the plane and v2 v 2 is the velocity vector of the wind. the angle between v1 v 1 and v2 v 2 is pi/4. determine the resultant speed . Question on Resultant Velocity

The vector between them is the displacement of the satellite. We take the radius of Earth as 6370 km, so the length of each position vector is 6770 km. Figure 4.2.3: Two position vectors are drawn from the center of Earth, which is the origin of the coordinate system, with the y-axis as north and the x-axis as east.
Velocity is present in many aspects of physics, and we have created many calculators about it! The first velocity is the so-called terminal velocity, which is the highest velocity attainable by a free-falling object.Terminal velocity occurs in fluids (e.g., air or water) and depends on the fluid's density.Step 2: Calculate the magnitude of the resultant using Pythagoras = 5.4 Step 3: Calculate the angle using trigonometry. θ = 21.8. Step 4: Write the answer in full giving both magnitude and direction of the velocity and all units. The swimmer's velocity is 5.4 ms-1 at 22 o to the horizontal directionTo find the vertical component of the velocity, we'll use s i n θ = opposite hypotenuse = v y v . The hypotenuse is the magnitude of the velocity 24.3 m/s, v , and the opposite side to the angle 30 ∘ is v y . sin. . θ = v y v .Resultant velocity, on the other hand, is the vector sum of all individual velocities acting on an object. It takes into account both the magnitude and direction of each velocity component. Consider a scenario where an object is moving in a straight line at a certain speed, and suddenly a force is applied to change its direction. The resultant .When the projectile reaches a vertical velocity of zero, this is the maximum height of the projectile and then gravity will take over and accelerate the object downward. . Resultant force on Earth’s surface, of the attraction by the Earth’s masses, and the centrifugal pseudo-force caused by the Earth’s rotation. bilateral symmetry: the . The fundamental equation that powers the Resultant Velocity Calculator is: v_f = v_i + a*t. where: v_f is the final velocity (magnitude and direction), v_i is the initial velocity (magnitude and direction), a is the acceleration (positive for speeding up, negative for slowing down), t is the time in seconds.
resultant velocity resultant speed formulaIn either case, the resultant is the same. Using the same scale we used to construct the 60 km/h and 80 km/h velocity vectors on the diagram, we measure the length of the resultant. We will find that the resultant corresponds to a velocity of 100 km/h. The resultant velocity of the airplane relative to Earth is 100 km/h.

practice problem 2. A swimmer heads directly across a river swimming at 1.6 m/s relative to still water. She arrives at a point 40 m downstream from the point directly across the river, which is 80 m wide. Determine.. the speed of the current. the magnitude of the swimmer's resultant velocity.resultant velocitypractice problem 2. A swimmer heads directly across a river swimming at 1.6 m/s relative to still water. She arrives at a point 40 m downstream from the point directly across the river, which is 80 m wide. Determine.. the speed of the current. the magnitude of the swimmer's resultant velocity.
resultant velocity|resultant speed formula
PH0 · what does resultant velocity mean
PH1 · resultant velocity problems
PH2 · resultant velocity example
PH3 · resultant velocity definition
PH4 · resultant velocity calculator
PH5 · resultant speed formula
PH6 · resultant speed calculator
PH7 · how to calculate resultant force
PH8 · Iba pa